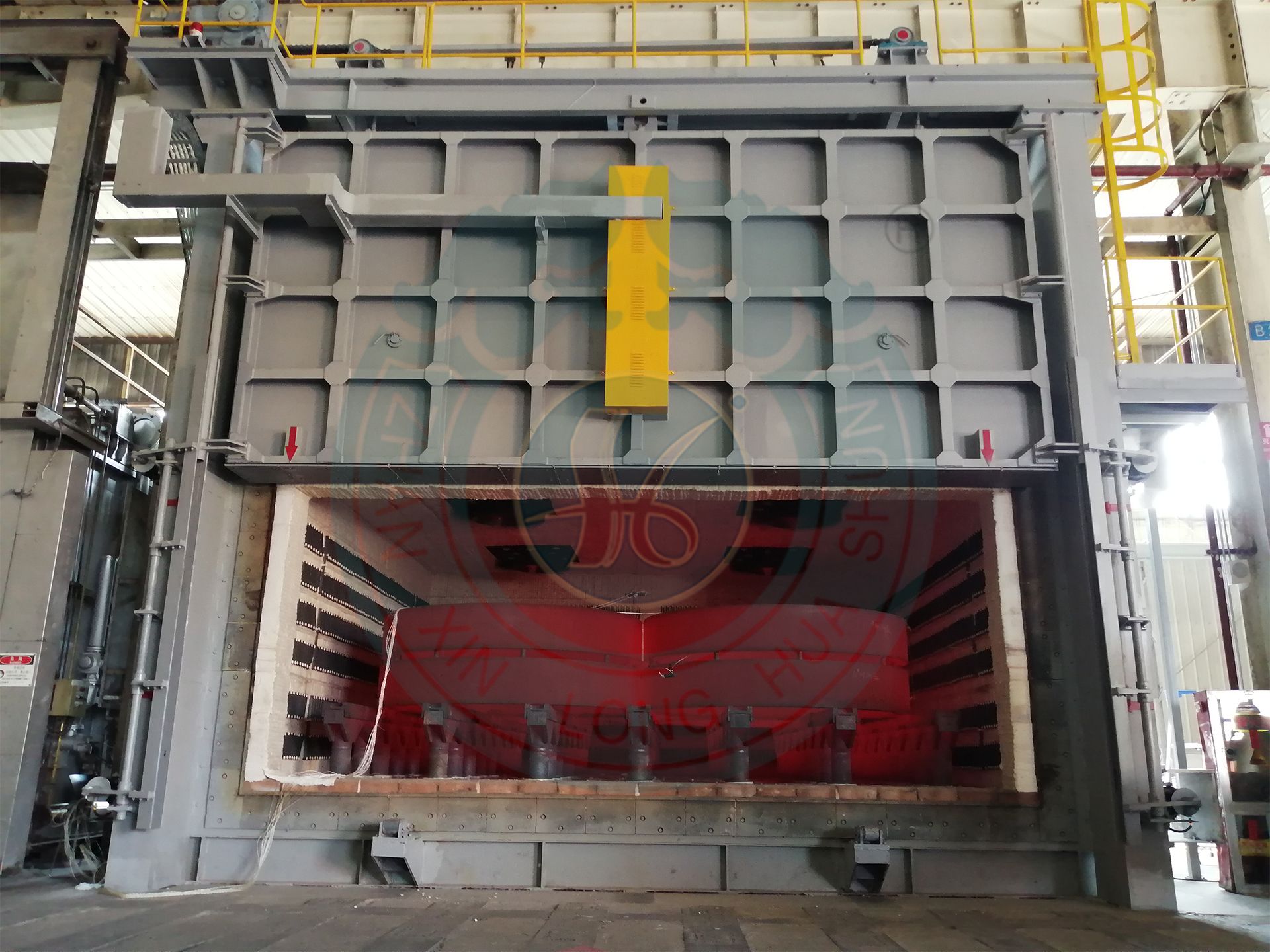
- Chamber Gas Heating Furnace
Chamber Gas Heating Furnace
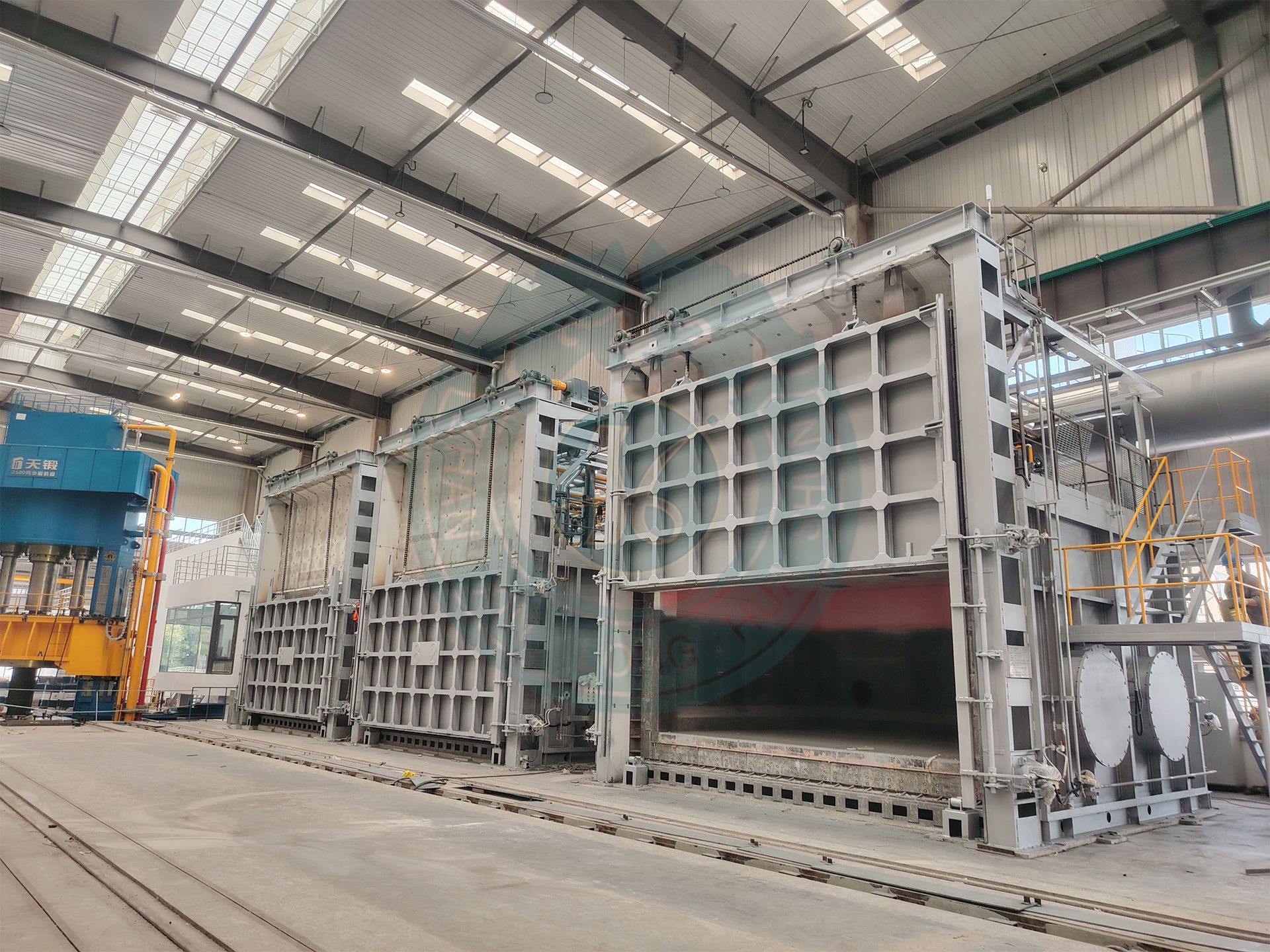


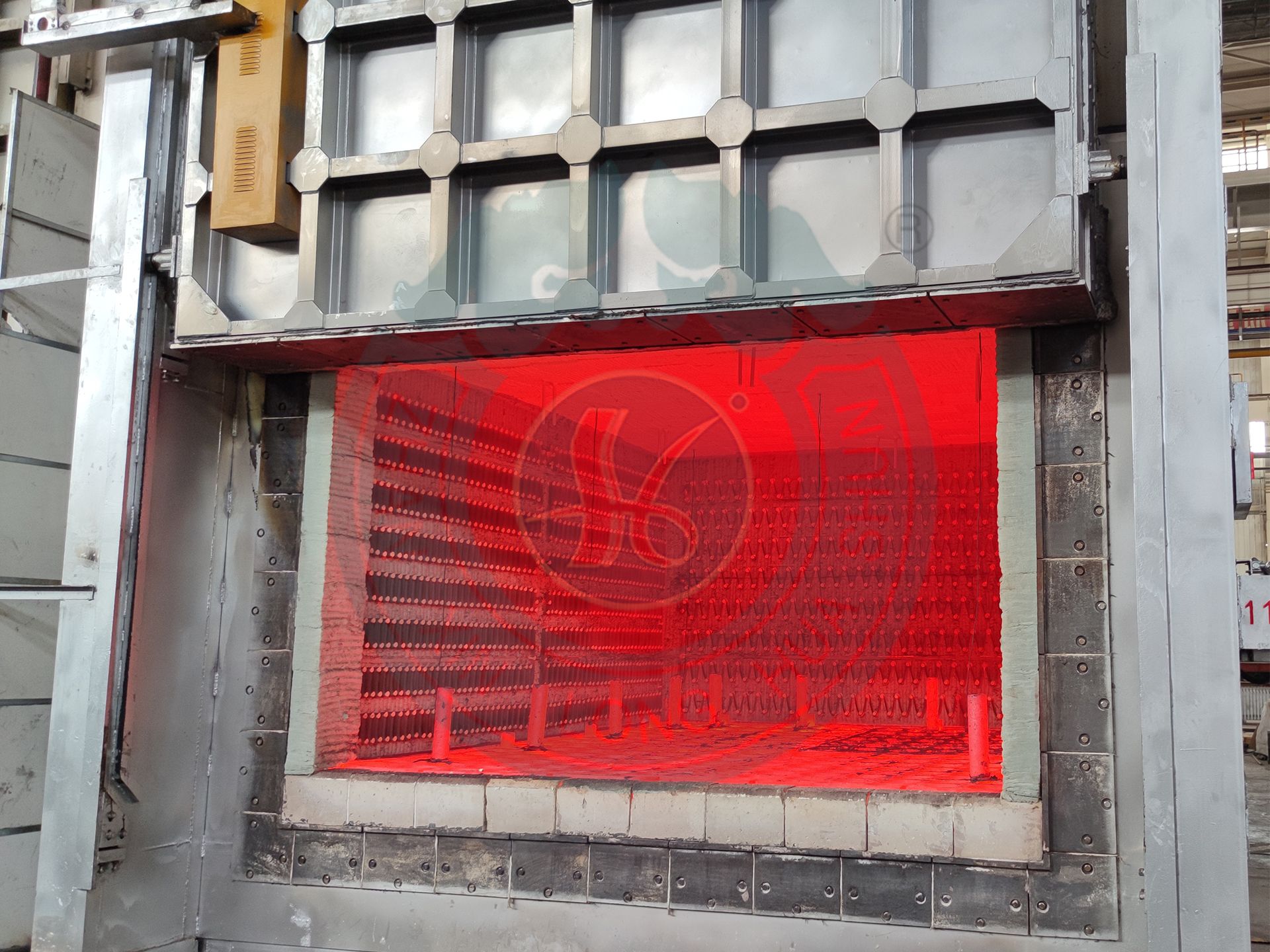
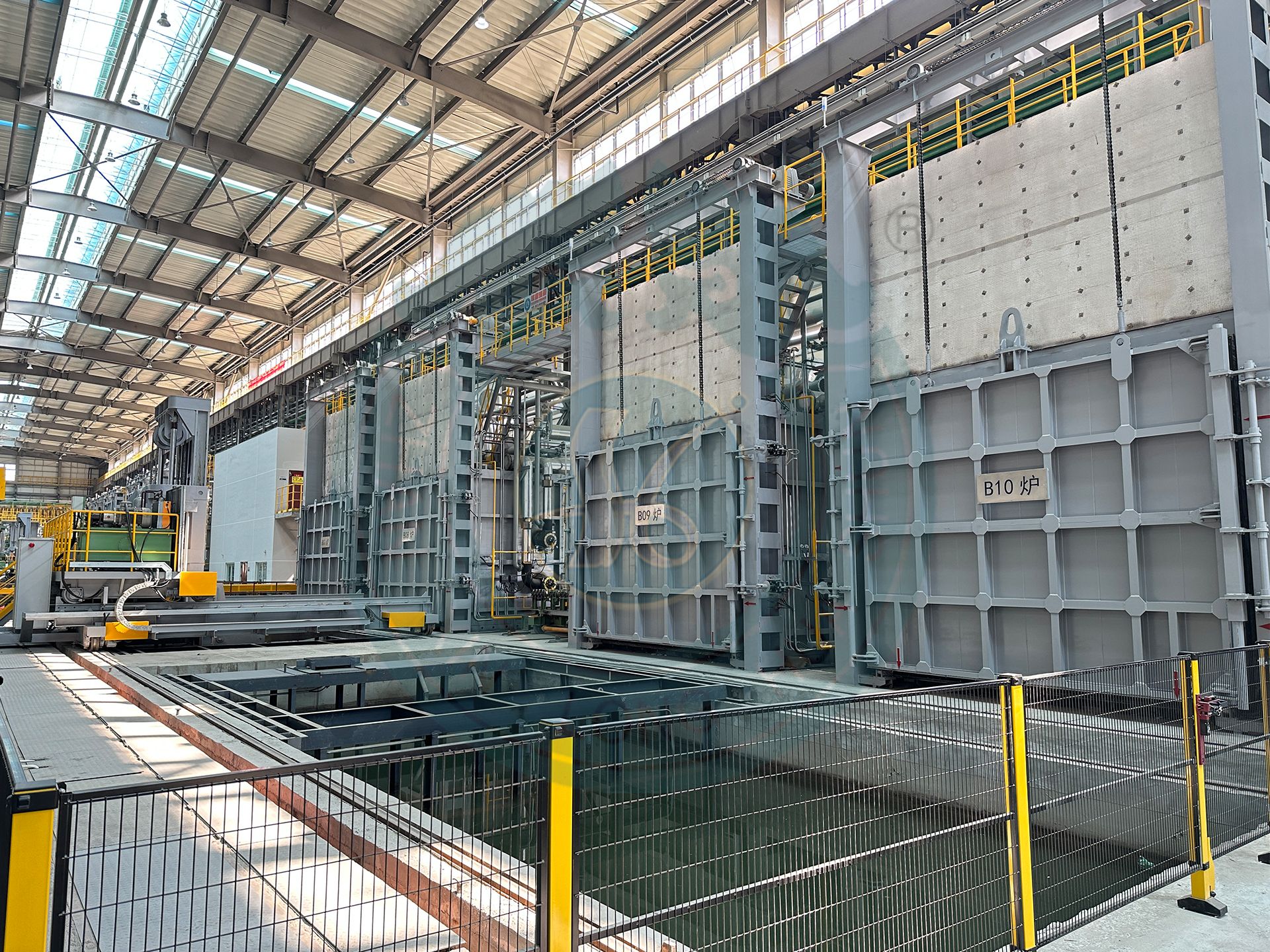
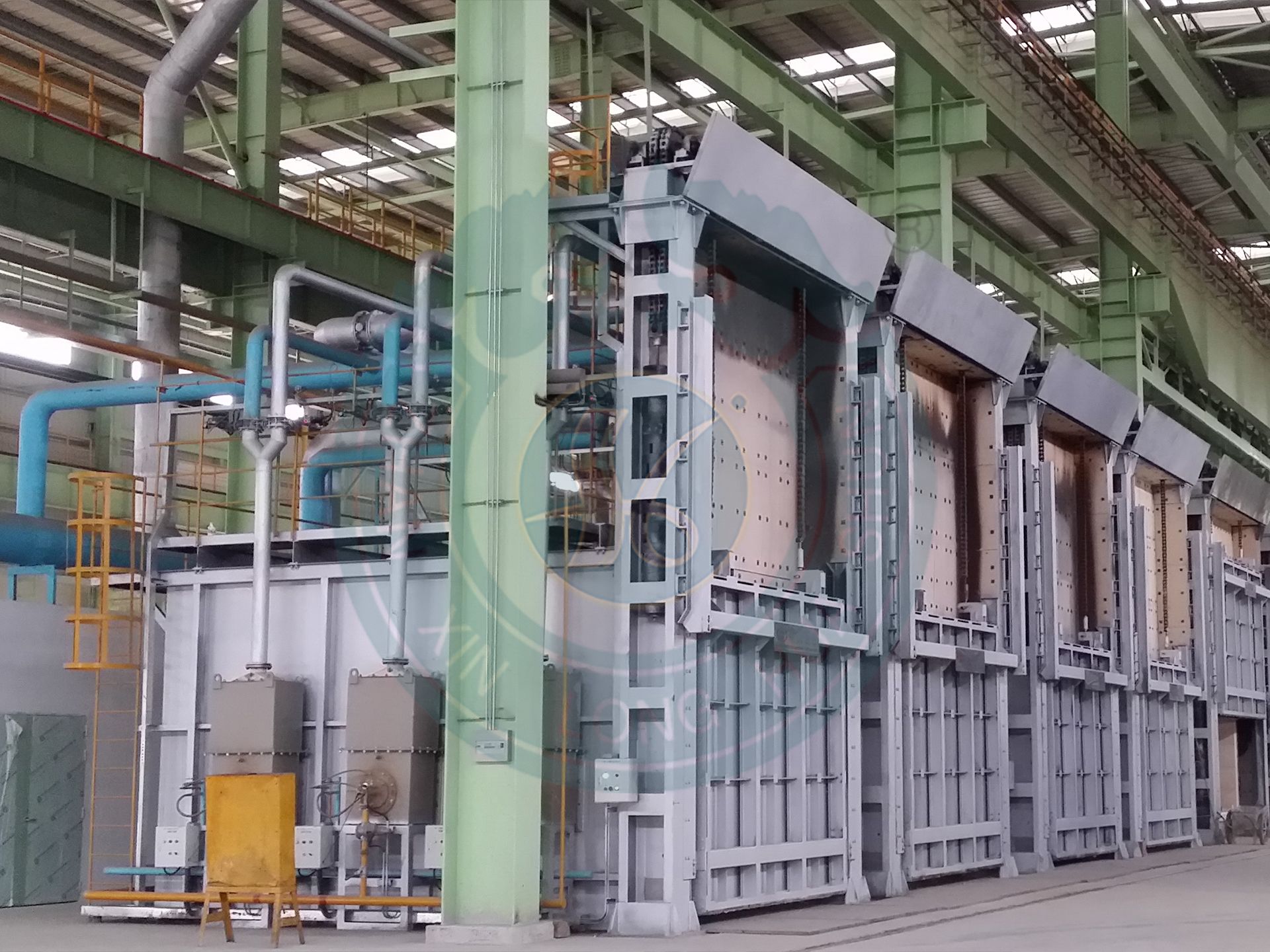
A chamber gas heating furnace is an intermittent heat treatment equipment that uses gas (natural gas, liquefied gas, etc.) as the heat source. It combines the structural characteristics of a chamber furnace with the high efficiency of gas heating, and is suitable for medium to high temperature, rapid heating, and low-cost production scenarios.
1. Efficient combustion and rapid heating
High heat load design: The power density of the gas burner is high (up to 200-500 kW/m ³), and the heating rate is 30% -50% faster than that of the electric furnace (such as only 2-3 hours for 0~1200 ° C).
Thermal efficiency optimization: By using waste heat recovery devices and requiring fewer sealing surfaces, the thermal efficiency can reach 60% -75% (compared to traditional gas stoves which require 40-50%).
2. Significant fuel economy
Low operating costs: The cost of natural gas is about one-third to one-half of electricity bills (calculated based on the same calorific value), making it suitable for large-scale heat treatment needs.
Wide fuel adaptability: can switch between natural gas, liquefied gas, coke oven gas, etc., to adapt to different energy conditions in different regions.
3. Outstanding high-temperature processing capability
High temperature resistant structure: The burner and furnace lining are made of silicon carbide/corundum mullite material, with a maximum temperature of 1200-1350 ° C (usually ≤ 1200 ° C for electric furnaces).
High power output: Single furnace power can reach several hundred kilowatts to several megawatts, suitable for rapid heating of heavy workpieces.
4. Limited process flexibility but high stability
Temperature control accuracy: ± 5-10 ° C (slightly lower than the ± 1-5 ° C of electric furnaces), but the temperature stability is better (due to the large thermal inertia of gas).
Atmosphere compatibility: An additional atmosphere control system (such as introducing nitrogen to prevent oxidation) is required, but the open combustion environment limits the application of high-purity atmospheres.
Equipment usage: Heating, normalizing, quenching, tempering, stress relief annealing, spheroidizing annealing, etc.
Applicable industries: head, flange, locomotive industry, nuclear power equipment, wind power equipment, military equipment, forgings and other industries. Heating energy: gas, electricity.
Furnace door opening and closing: lifting gate type, side opening translation, rotating split type. Lining insulation: full fiber structure.
Control mode: upper computer+configuration software DCS distributed control (automatic+manual), multiple group control, PID control. Working size: Designed according to the workpiece size and furnace loading capacity as needed, or based on the size provided by the user. Maximum temperature: 1350 ℃


 Home
Home